The Role of Open Access data in Geospatial Electrification Planning and the Achievement of SDG7
An OnSSET-Based Case Study for Malawi
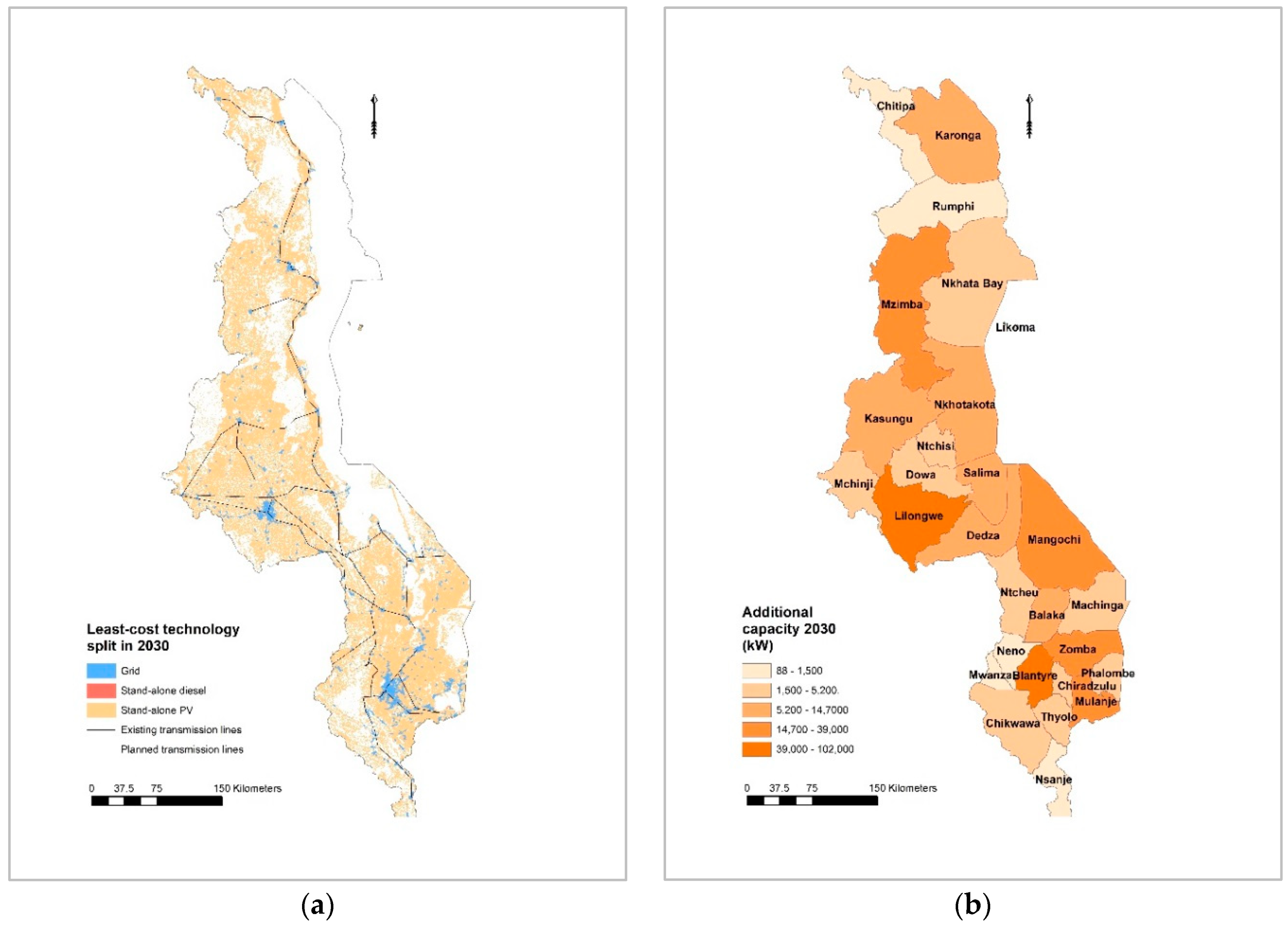
Achieving universal access to electricity is a development challenge many countries are currently battling with. The advancement of information technology has, among others, vastly improved the availability of geographic data and information. This new publication provides an overview of open access geospatial data and GIS based electrification models aiming to support SDG7, while discussing their role in answering difficult policy questions. Upon those, an updated version of the Open Source Spatial Electrification Tool is introduced and tested against the case study of Malawi. At a cost of $1.83 billion the baseline scenario indicates that off-grid PV is the least cost electrification option for 67.4% Malawians, while grid extension can connect about 32.6% of population in 2030. Sensitivity analysis however, indicates that the electricity demand projection determines significantly both the least cost technology mix and the investment required, with the latter ranging between $1.65–7.78 billion.
Read the full publication here .

