Modeling Tools
Three modeling tools have been developed within the KTH-CSP-TEA group in order to:
1. Optimize the design and operation of power plants,
2. Model electricity market scenarios and power generation mix and,
3. Understand the thermo-mechanical behavior of power plant components during transient operation.
The tool at power plant level is called DYESOPT and it relies on the integration and calibration of inputs such as local electricity demand, market prices, desing and operation related economics. The tool at market level is called EDGESIM and it provides full electricity market modeling for detemining optimal power generation mix during given trasing periods. The tool at component level is called ST3M and its centered around steam turbine thermal behavior and start-up time optimization. Below you will find a more detailed description about each tool.
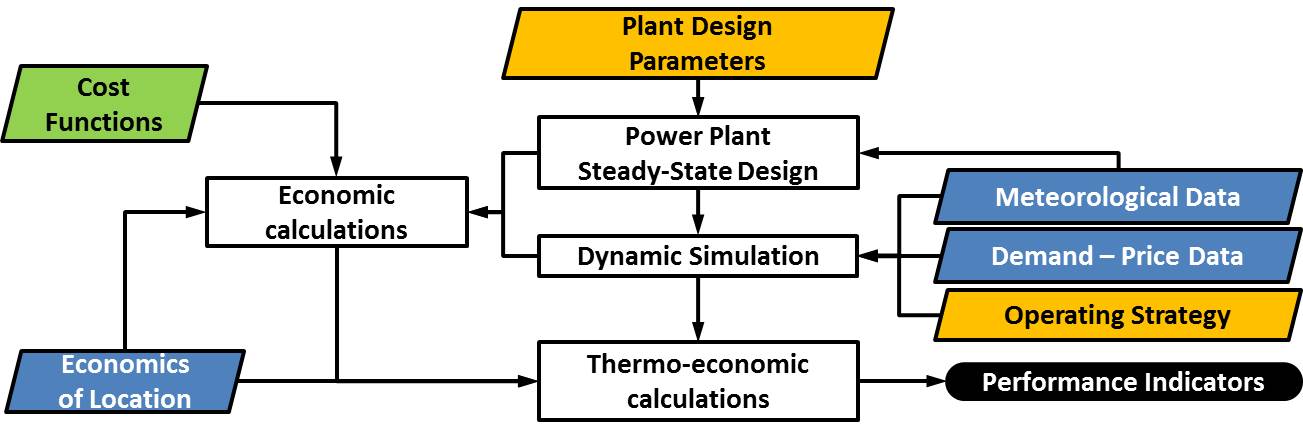
DYESOPT
DYESOPT stands for DYnamic Energy System OPTimizer. This tool has the capability of modeling the transient operation of power plants and assess their thechno-economic performance with respect to operation strategies and economic feasability. DYESOPT is based on detailed equations of typical power plant components in order to realistically account for power plant behavior. Furthermore, DYESOPT is coupled with a multi-objective optimizer that allows trade-offs of conflicting design aspects to be observed. All of this with the purpose of assessing the user in the optimal configuration of the existing or to-be existing power plant. Below is a flow chart of how DYESOPT works:
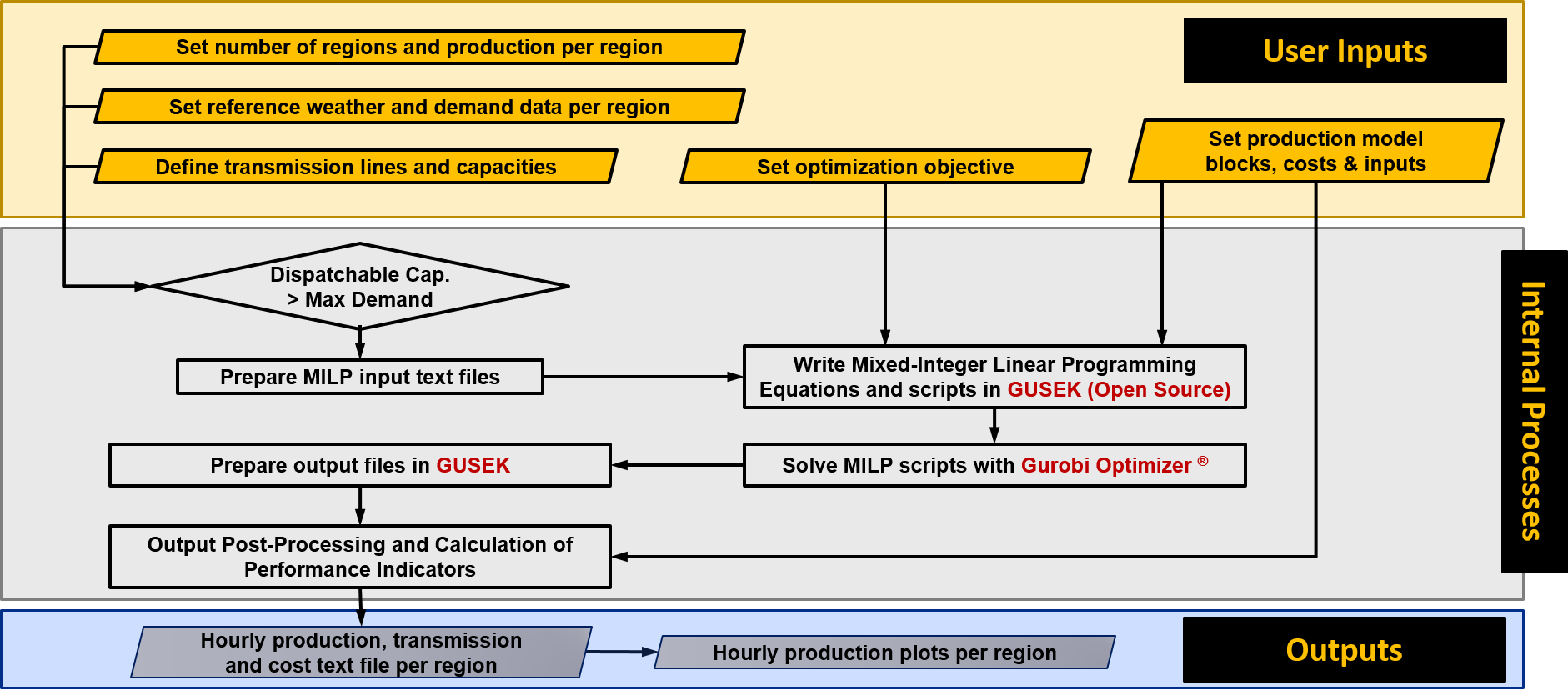
EDGESIM
EDGESIM stands for Electricity Distribution and GEnerator SIMulator. This tool has the capability of evaluating the performance of given power plant technologies in liberalized electricity markets. Essentially, this model is a power plant dispatching model that calculates the operation of a given set of power plant in order to satisfy the demand with the lowest cost. As no proference is given to any technology, this approach allows the true viability of the different power plants to be determined.
EDGESIM simulates a specific electricity market using a multi-node power grid model. In other words, a certain geographical area is represented by a node in the power system, in which a time-dependent load requirement and installed generation capacities of different power plant types are included. Using the available installed generation capacities, the load in each node is then sought to be met for each hour of the simulated time period using the available generation capacities in the power system, subject to inter-regional transmission capacity restraints (i.e. between nodes). Each generation type is associated with a marginal cost of power production and the tool seeks to minimize the total generation cost within each simulated hour, comparable to what is in actuality achieved through the hourly market clearing process at the power exchange. EDGESIM employs linear programming software for the optimization of power plant recruitment for each simulated hour, as part of the overall working process of the tool.
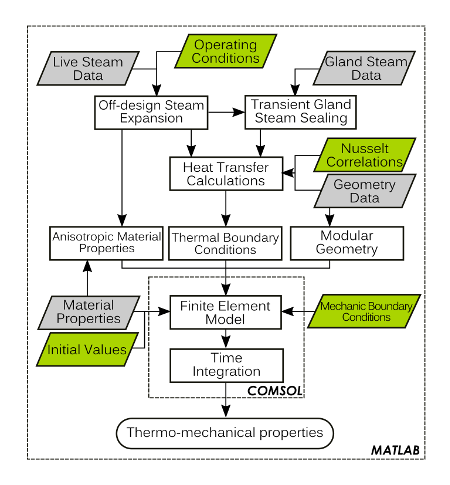
ST3M
ST3M stands for Steam Turbine Thermal Transient Model (STTTM=ST3M). This tool has the capability of evaluating the thermal conditions of a given steam turbine model during its transient operation. Basically, this model is a thermo-mechanical model that is able to determine the thermal stress and differential expansion evolution in a turbine during start-up and shut-down operation.