H2020 Pump Heat
Performance Untapped Modulation for Power and Heat via Energy Accumulation Technologies with a consortium consisting of 14 participants from 8 countries

Funded by: European Commission
Time period: 2017-2020
Project members:
UNIGE Università Degli Studi Di Genova
RINA-C RINA Consulting
KTH Royal Institute of Technology
AUTH Aristotle University of Thessaloniki
LSC Limmat Scientific AG
AEN Ansaldo Energia SPA
IREN IREN SPA
ORLEN Polski Koncern Naftowy ORLEN SA
MHPSE Mitsubishi Hitachi Power Systems Europe GmbH
NOV Novener
MAYE NV MAYEKAWA Europe SA
SIEME Siemens Industry Software SAS
i-TES i-TES SRL
AL Alfa Laval Lund AB
Background
Natural gas fired Combined Cycle (CC) power plants are currently the backbone of EU electrical grid, providing most of regulation services necessary to increase the share of non-programmable renewable sources into the electrical grid. As a consequence, Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and Utilities are investigating new strategies and technologies for power flexibility. Current research activities for CCs flexibility enhacement (e.g. power ramp augmentation, Minimum Electrical Load - MEL - reduction) focus mainly on the GT and extend the operational envelop of this component, which is primarily constrained by emissions (typically, CO at low load and NOx formation at full load). On the other hand, existing cogenerative CCs are usually constrained by thermal user demand, hence can provide limited services to the grid. At the same time, CHP plants are highly promoted for their high rate of energy efficiency (> 90%) and combined with district heating network are a pillar of the EU energy strategy. PUMP-HEAT aims at an innovative approach to enhance CC flexibility through bottoming cycle innovations, applicable also to cogenerative CCs.
Aim and objectives
The main aim of PUMP-HEAT is to develop and demonstrate up to TRL 6 in the relevant environment (a real Combined Cycle Cogenerative plant) an innovative, easily scalable, economically viable and replicable plant layout based on the integration of heat pumps (HP) and thermal energy storage, to un-tap Combined Cycle (CC) potential flexibility through low-CAPEX balance of plant innovations.
The Objectives are:
- To un-tap the unexploited reserve of flexibility in cogenerative CCs, and to further enhance turn-down ratio and power ramp capabilities of power oriented CCs.
- PUMP-HEAT project proposes the demonstration of an innovative concept based on the coupling of a fast-cycling highly efficient heat pump (HP) with CCs.
- The integrated system features thermal storage and advanced control concept for smart scheduling.
Outcomes
The complete overview of the 7 workpackages are shown below, KTH acts as the WP3 leader, led by Assist. Prof. Dr. Justin Chiu, and KTH will have a large contribution in WP1 through Dr. Rafael Guedez, with supportive roles in WP4 and WP6
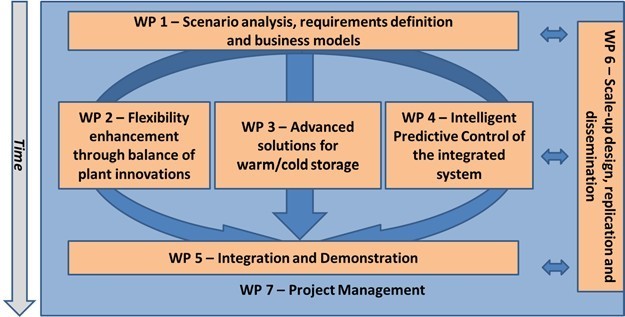
In general, the CC integration with a HP and a cold/hot thermal storage brings to a reduction of the MEL and to an increase in power ramp rates, while enabling power augmentation at full load and increasing electrical grid resilience and flexibility. The PUMP-HEAT concept could stop the mothballing of EU Combined Cycles, pushing new installations and the retrofitting of already existing power plants giving a second chance to such these crucial energy systems in the current and future energy scenario. The PUMP-HEAT technology will be able also to have technological impacts on the CC and GT power plants increasing the annual and seasonal efficiency up to 5%, reducing OPEX of 3%, increasing the possibility for such plants to sell more electricity on the Regulation and Ancillary Services Electrical Market, thanks to their increased flexibility and fast responsivity (about a 30% of the generation could be sold on these markets at a 50% higher revenue) and reducing the number of start-ups of 5-10% and the related extra costs, equivalent operating hours (EOH) and wear.
The PUMP-HEAT Combined Cycle aims to become a new paradigm for GT and CC power plants recognized in both the technical and academic panoramas.
Publications
Please see the link below for the complete list of publications:
Project contact persons
Read more about the project on pumpheat.eu


